購入した書籍「インフラCI実践ガイド」を試した際のメモの続きです。

第7章のCIのパイプライン後半になります。
7.2 さまざまな問題を検知する
7.3.1 規約「非」準拠を検知する
演習環境の上でAnsibleを例にコーディング規約のエラーがどのように検知されるかを確認する。
想定作業と実装
「CMSの初期DBのバックアップを保存しておいてほしい」
という依頼があることを想定して進めてます。
初期DBは「/opt/ketchup/app-contents/contents/data/default.db」にあるので、これをdefault.db.originとして保存する処理を追加します。
テスト側ではdefault.db.originが存在しているかを確認します。
編集が必要なファイルは2つです。
「/roles/ketchup/tasks/main.yml」と「/roles/ketchup/tasks/unit_test.yml」
変更作業
演習ではあえてnameをつけないであえてパイプラインでのlintのチェックでエラーにしています。
[root@infraci ketchup-vagrant-ansible]# vim roles/ketchup/tasks/main.yml
- name: Backup default.db file to default.db.origin
copy:
src: "{{ ketchup_home }}/{{ ketchup_data_dir }}/default.db"
dest: "{{ ketchup_home }}/{{ ketchup_data_dir }}/default.db.origin"
remote_src: true
[root@infraci ketchup-vagrant-ansible]# vim roles/ketchup/tasks/unit_test.yml
- name: Retrive default.db.origin stat
stat:
path: "{{ ketchup_home }}/{{ ketchup_data_dir }}/default.db.origin"
register: test_db_backup_file
- name: Check default.db.origin is exist or not
assert:
that:
- test_db_backup_file.stat.exists == true
msg: "default.db.origin is not exist"
[root@infraci ketchup-vagrant-ansible]# git commit -a -m "fixed unnamed tasks"
[master a85955b] fixed unnamed tasks
2 files changed, 17 insertions(+), 1 deletion(-)
[root@infraci ketchup-vagrant-ansible]# git push
Username for 'http://192.168.33.10': root
Password for 'http://root@192.168.33.10':タスクにnameが正しくついていることが確認できます。
[root@infraci ketchup-vagrant-ansible]# ansible-playbook ketchup.yml --list-tasks
playbook: ketchup.yml
play #1 (ketchup): Install Ketchup TAGS: []
tasks:
repos_el : include task specific variables TAGS: []
repos_el : Install yum repositories TAGS: []
repos_el : Enable epel repository TAGS: []
packages_el : include task specific variables TAGS: []
packages_el : Install common packages TAGS: []
packages_el : Install nginx packages TAGS: []
ketchup : include task specific variables TAGS: []
ketchup : Create ketchup home directory TAGS: []
ketchup : Download ketchup app and contents from github TAGS: []
ketchup : Extract ketchup app TAGS: []
ketchup : Install ketchup configuration file TAGS: []
ketchup : Install bootstrap for systemd TAGS: []
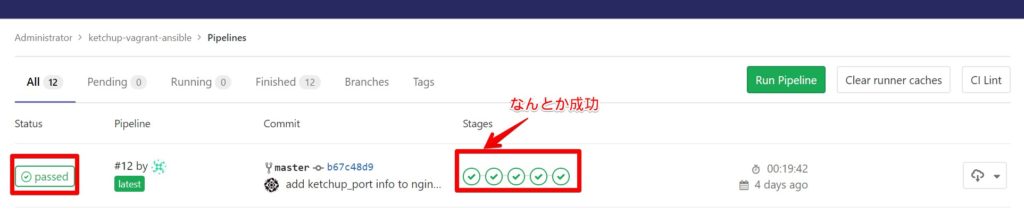
ketchup : Backup default.db file to default.db.origin TAGS: []パイプラインが正常に終わっていることを確認します。
※スぺルミスや記載漏れなどで何回か失敗しましたが、なんとか最終的にOKになりました。
7.3.2 デグレートを検知する
デグレート(リグレッション)の発生は一番避けたい現象の一つです。インフラCIにおけるパイプラインはデグレートを防止する有効な手段
7.3.3 連携(インテグレーション)の不備を検知する
例として以下を想定して連携の不備を検知する
- 2台のサーバは別々のチームが担当し、それぞれが責任を持つ
- ketchupのポートを8080に変更する依頼がきた
想定作業と実装
ポートを80から8080に変更します。
タスクとユニット側を修正します。
[root@infraci ketchup-vagrant-ansible]# cd ~/ketchup-vagrant-ansible/
[root@infraci ketchup-vagrant-ansible]# vim hosts/ketchup/inventory
[all:vars]
ketchup_host=192.168.33.12
ketchup_nginx_host=192.168.33.13
ketchup_port=8080
[root@infraci ketchup-vagrant-ansible]# vim hosts/ketchup/test_inventory
[all:vars]
ketchup_host=192.168.33.14
ketchup_nginx_host=192.168.33.15
ketchup_port=8080
これだけだと、インテグレーションテストで失敗します。nginx側の設定も変更する必要がありるので修正します。
[root@infraci ketchup-vagrant-ansible]# vim roles/nginx/templates/ketchup.conf.j2
server {
listen {{ nginx_http_port }};
server_name localhost;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
location / {
proxy_pass http://{{ ketchup_host }}:{{ ketchup_port }}/;
}
}
[root@infraci ketchup-vagrant-ansible]# git commit -a -m "fixed unnamed tasks"
[master a85955b] fixed unnamed tasks
2 files changed, 17 insertions(+), 1 deletion(-)
[root@infraci ketchup-vagrant-ansible]# git push
Username for 'http://192.168.33.10': root
Password for 'http://root@192.168.33.10':パイプラインが成功することを確認します。
7.4 パイプラインを編集する
パイプラインそのものを拡張する方法について説明されてます。
sample_stage1というステージを追加するとともに、Sample_job1という処理を追加しています。
[root@infraci ketchup-vagrant-ansible]# vim ./.gitlab-ci.yml
---
stages:
- lint
- unit_prepare
- unit_test
- int_deploy
- int_test
- sample_stage1
variables:
CONTAINER_IMAGE: c7-systemd
CONTAINER_IMAGE_PATH: ${CI_REGISTRY}/${CI_PROJECT_PATH}/${CONTAINER_IMAGE}
Sample_job1:
stage: sample_stage1
image:
name: irixjp/lint-rules:latest
script:
- echo "Hello Stage!"
tags:
- docker
[root@infraci ketchup-vagrant-ansible]# git commit -a -m "add a new stage to pipeline"
[root@infraci ketchup-vagrant-ansible]# git pushgitでpushしてからパイプラインが成功するのを確認します。先ほど追加したステージが追加されていることと、その処理の中でHello Stage!が実行されていることを確認します。
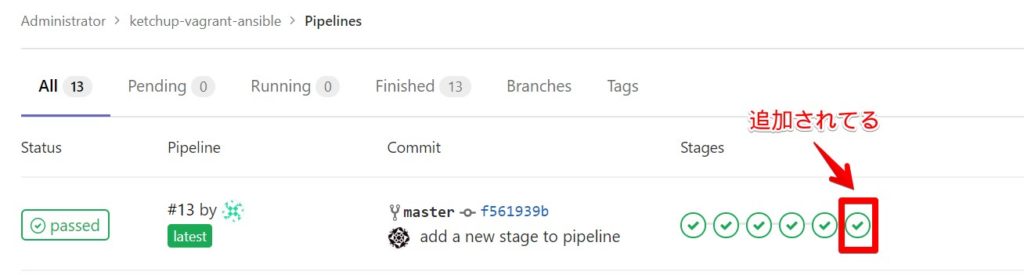
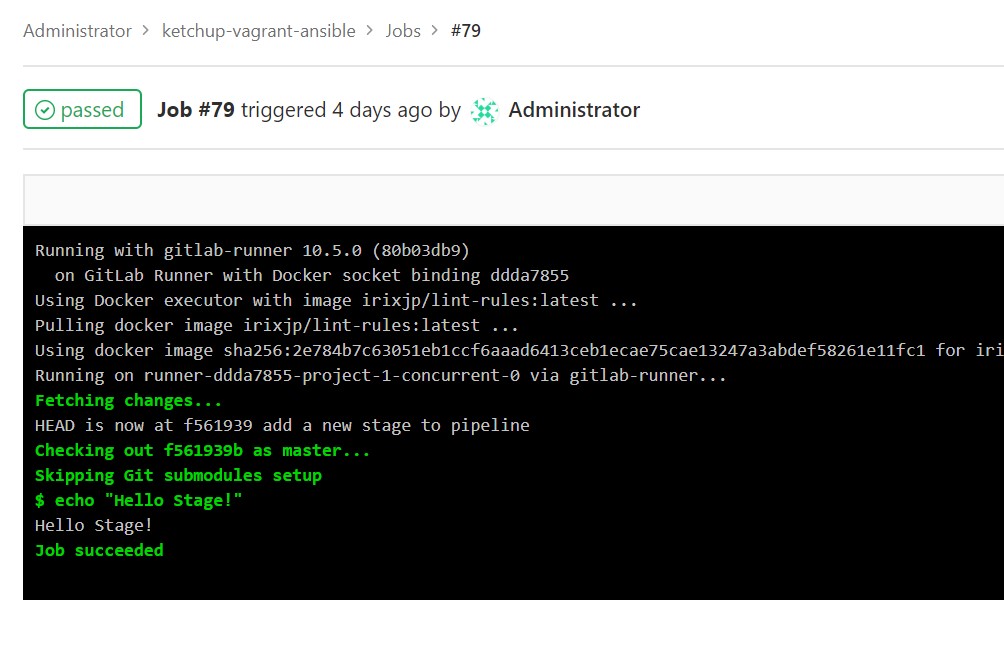
7.5 演習環境のクリア
書籍の通りに実行します。
7.6 まとめ
パイプラインとはCI(CD)に最適化されたジョブ管理ツール
パイプラインでプロジェクトの規約や各種手順を定義し、メンバーに強制することでプロジェクト全体の標準化を図れる
パイプライン自身も常に変化させる
やはり、プロジェクトメンバーに強制させれるというのが重要ですね!!
次回はいよいよ複数メンバーを想定した運用に入ります!
今回は以上となります。










コメント